Visualization for Machine Learning
Spring 2024
Perception for Design

Brain
“Visual thinking consists of a series of acts of attention, driving eye movements, and tuning our pattern finding circuits”, Colin Aware
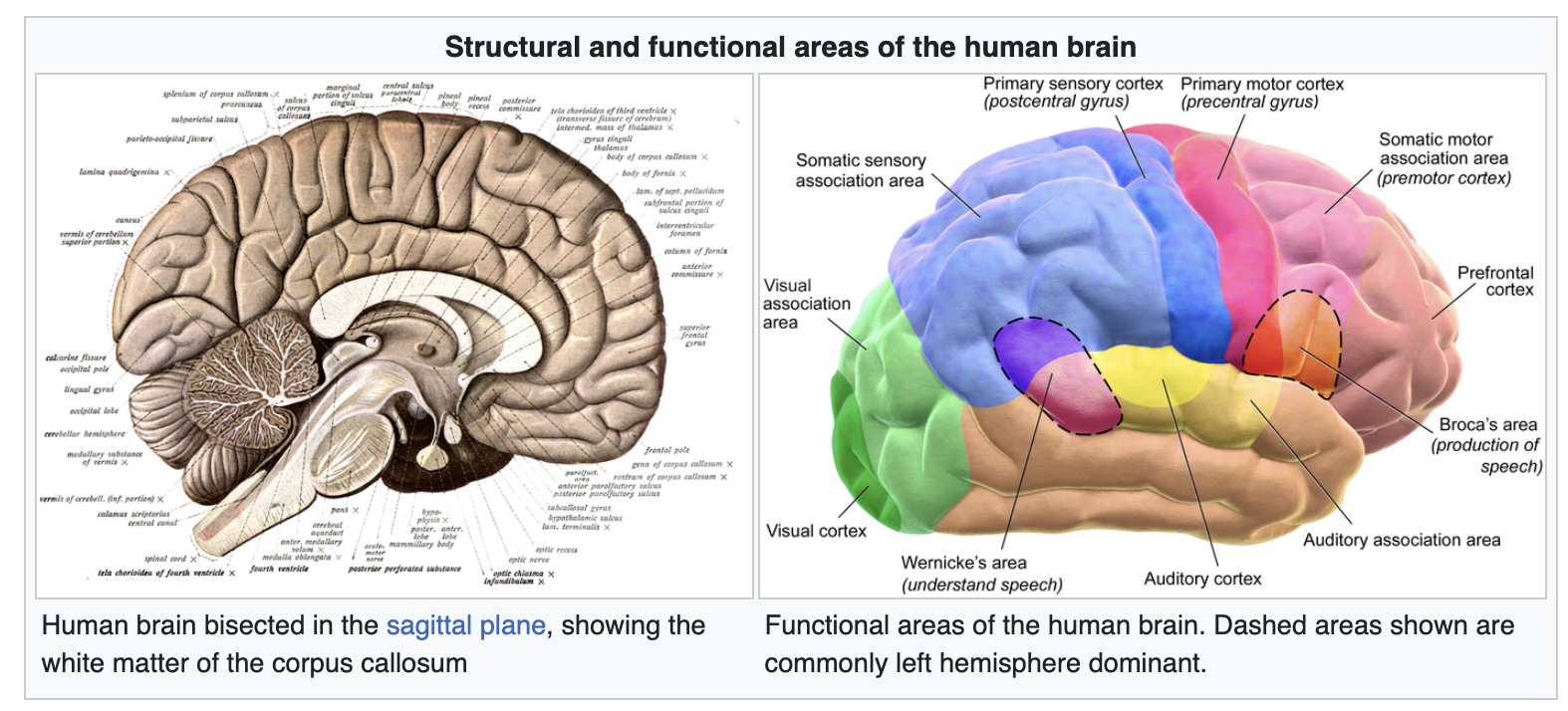
Image from Wikipedia: link
The Vision Brain
“Visual thinking consists of a series of acts of attention, driving eye movements, and tuning our pattern finding circuits”, Colin Aware
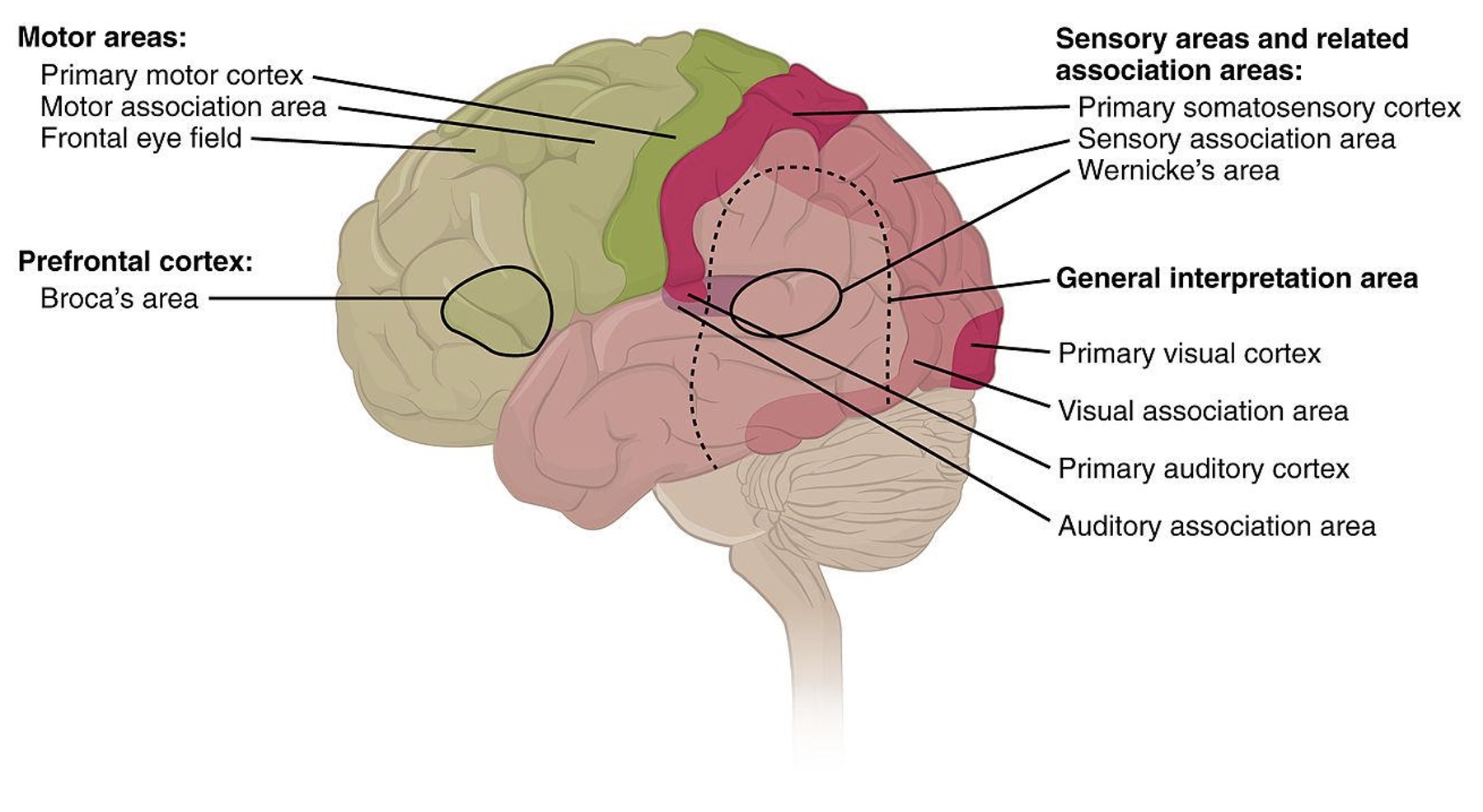
Image from Wikipedia: link
The Act of Perception
- Botton-Up and Top-Down Processes
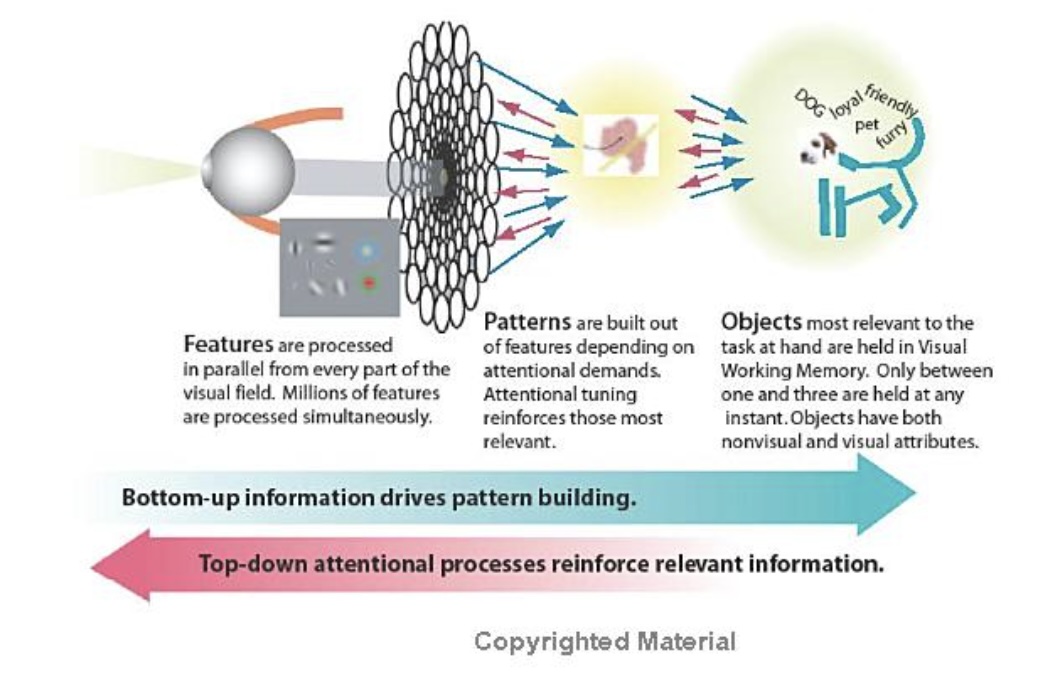
Material from Colin Ware’s book
The Act of Perception
- Bottom-up: information is sucessively selected and filtered into patterns as it passes a sequence of stages. Ware outlines three stages: 1) optical nerve to V1 Cortex; 2) use texture and colors to aggregate patterns; 3) visual objects are recognized in the visual working memory.
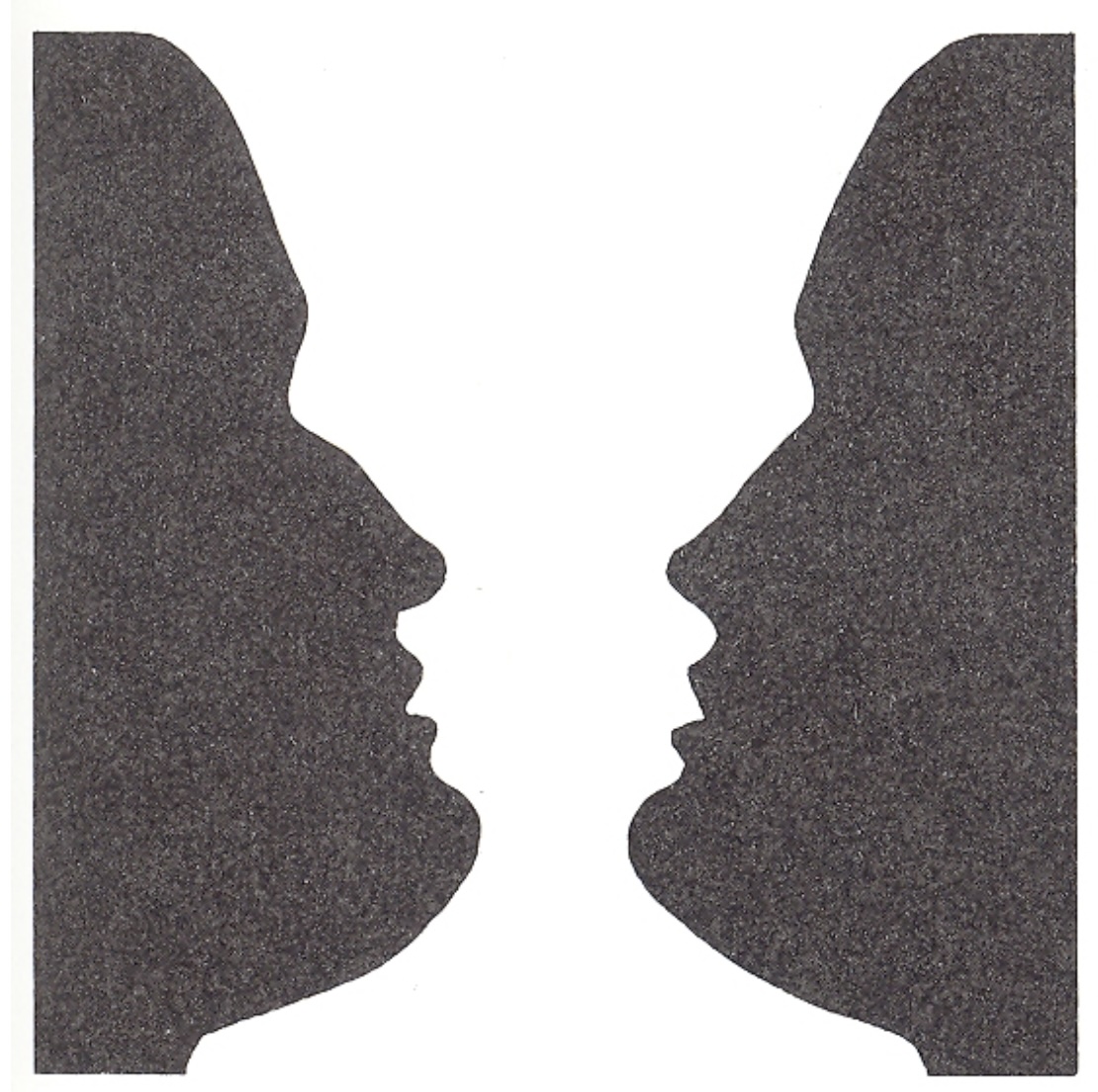

Image from the book: “Eye and Brain: The Psychology of Seeing”, Gregory
The Act of Perception
- Top-Down: Every stage of bottom-up processing contains a corresponding top-down process. Ware describes the process as “attention”. The dominant principle is that we only get the information that we need, when we need it.
Material from Colin Ware’s book
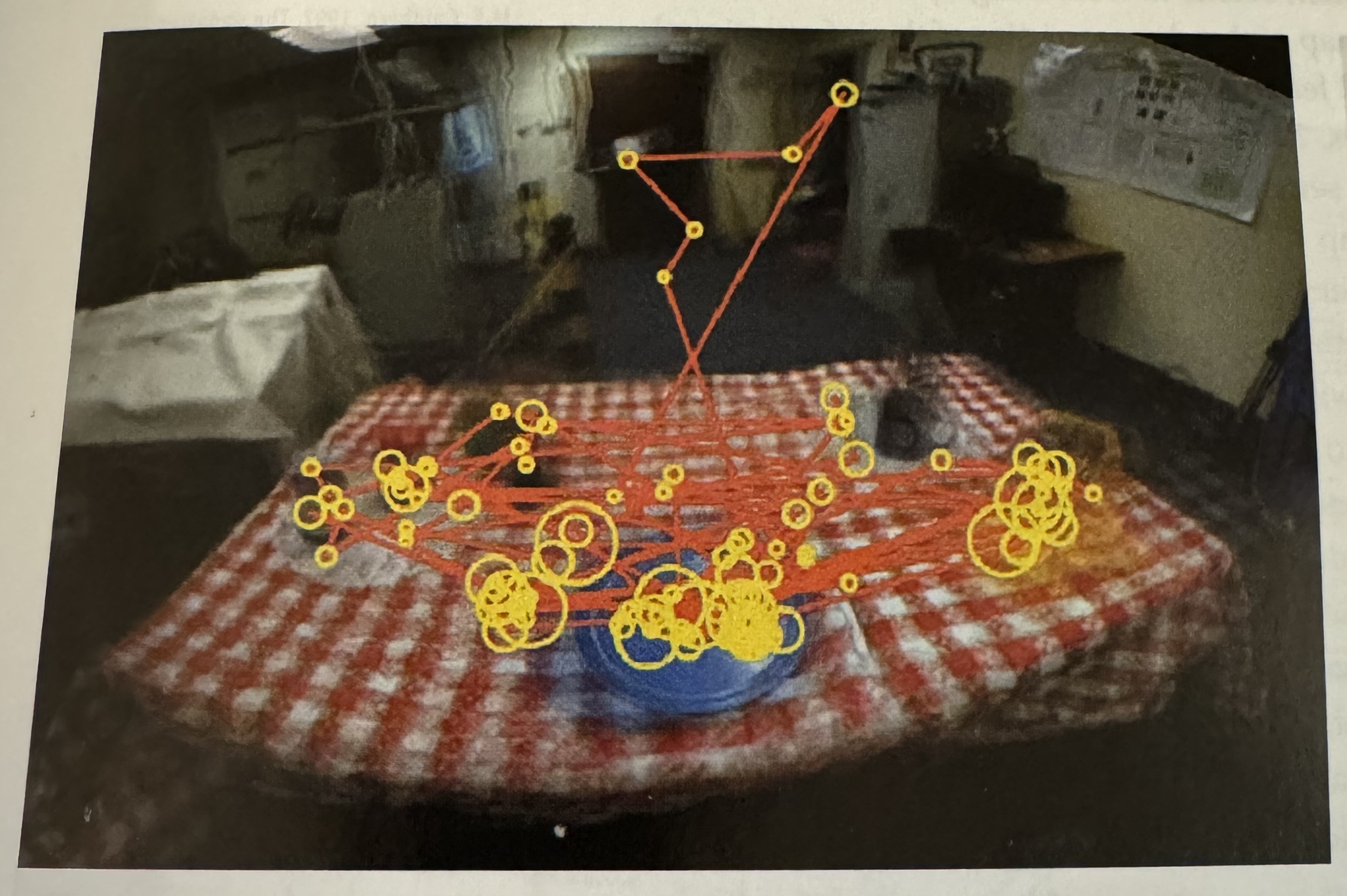
The Implications for Design
“Just-in-time visual queries” (Ware)
“One way to look at the brain operates is a set of nested loops. Outer loops deal with generality while inner loops process detail.” (Ware)
Material from Colin Ware’s book
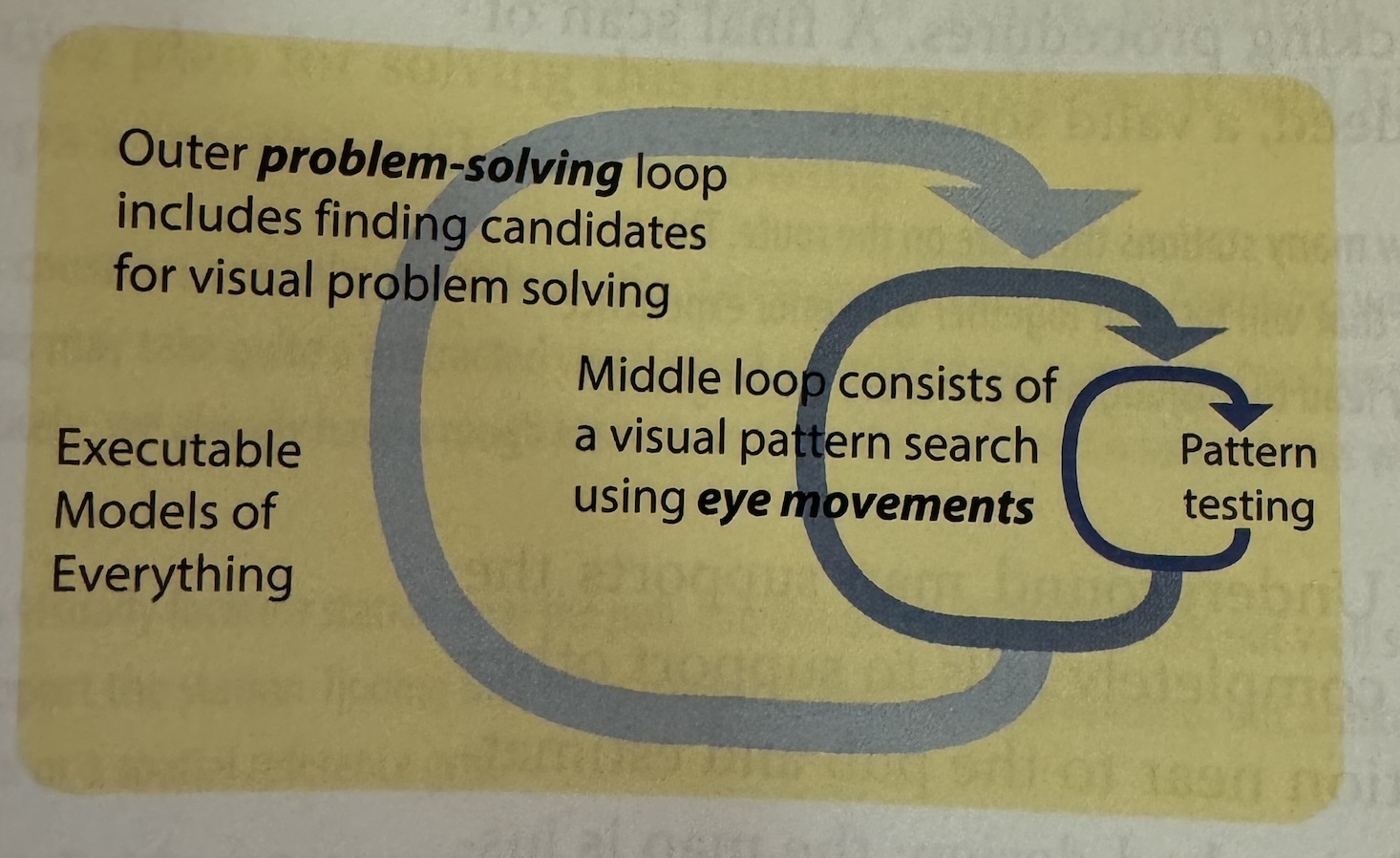
Low-Level Feature Analysis
- David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel won Nobel prize for this discovery.
Material from Colin Ware’s book
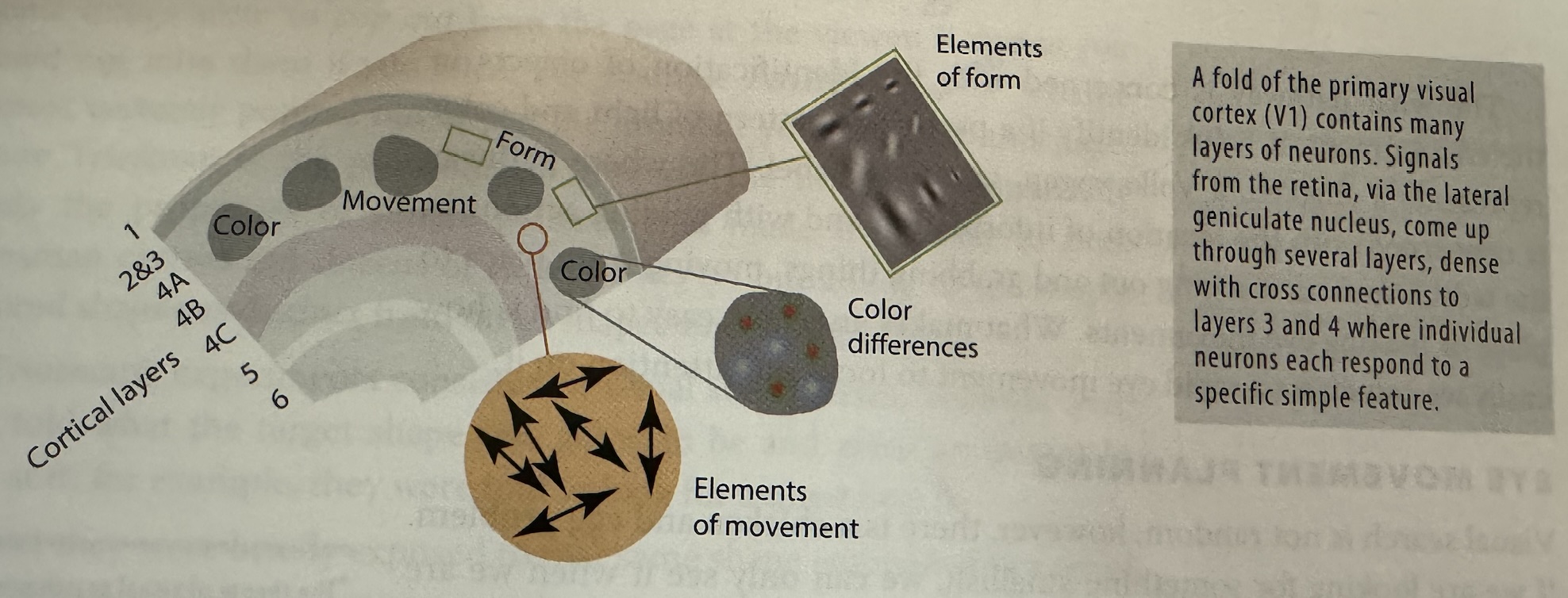
What and Where Pathways
- What: identification of objects in environment.
- Where: location of objects and eye movement.
Material from Colin Ware’s book
What Stands Out (Popout)
- Anne Triesman studied how to find patterns and shapes when surrounded by others.
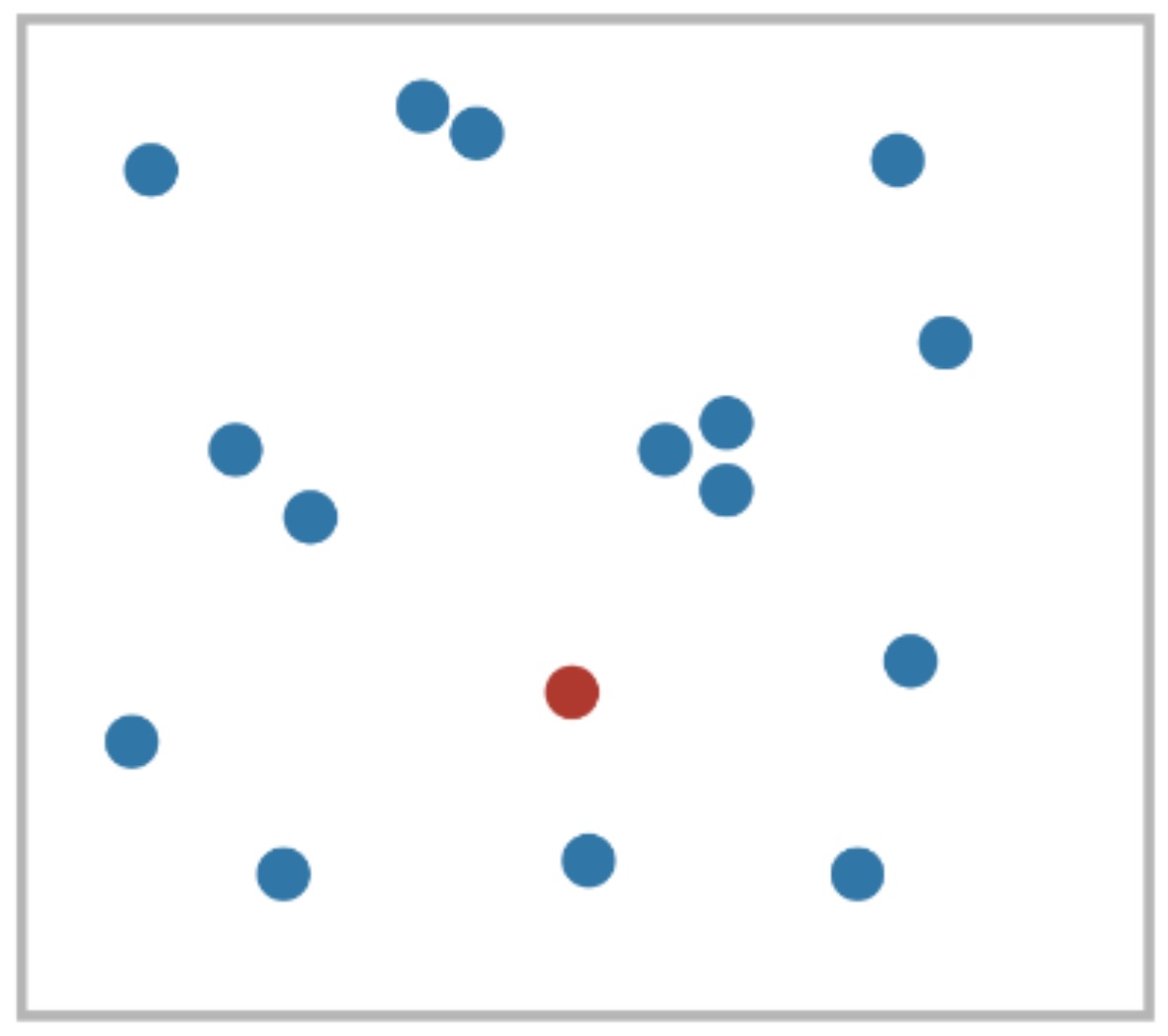
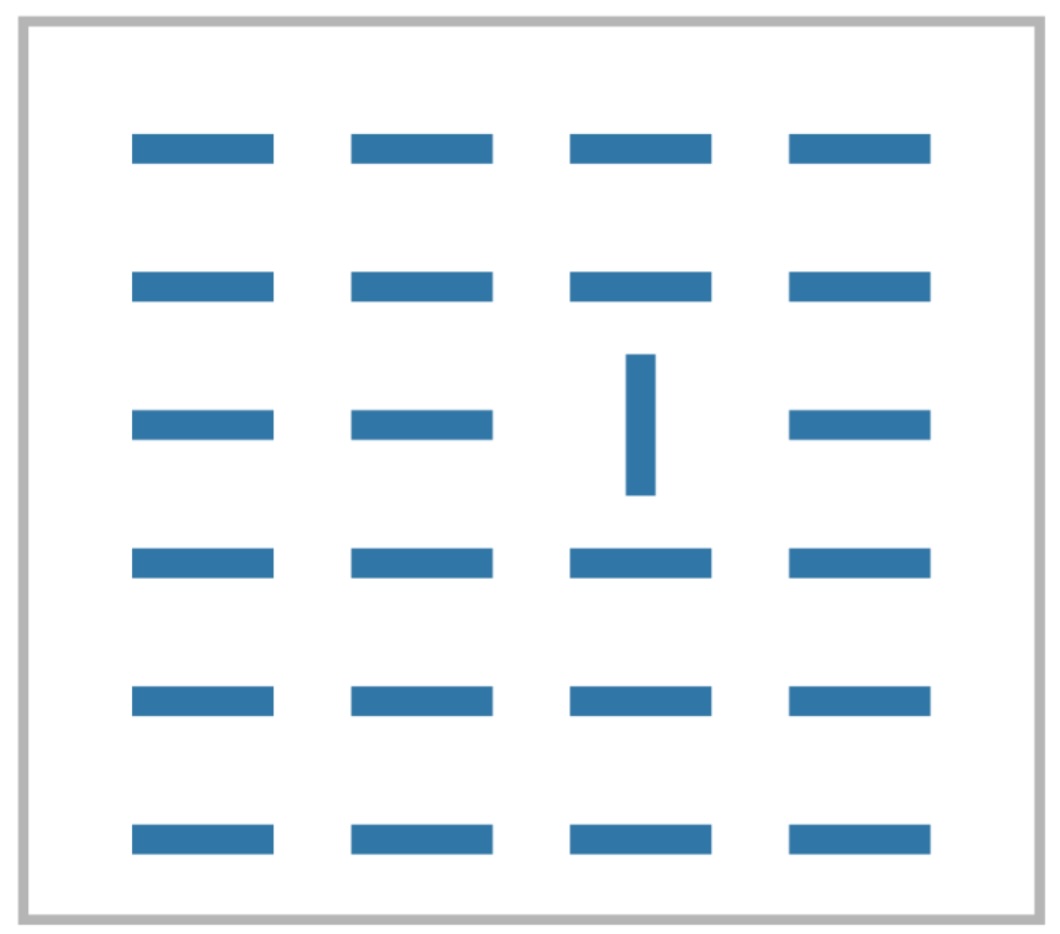
For some configurations the time did not depend on the number of distracters (pre-attentive).
Material from Colin Ware’s book
What Stands Out (Popout)

Material from Colin Ware’s book
The Gestalt Principles link, see video
- Visualization is a two-way street:
- We (the vis designer) bring something to the table.
- The human (end user) brings their prior experience.
- Design should take such prior experience into account!
- What is prior experience? Gestalt laws.
Material from Matt Berger
Closure
- We can complete incomplete shapes
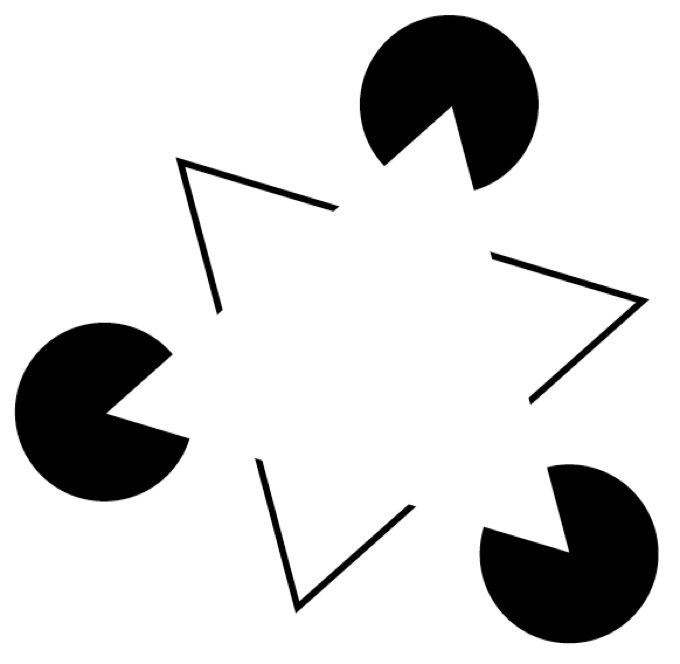
- Implications: visualizations can be unintentionally misleading! Conversely: sometimes only necessary to show sparse set of marks to convey trend (dot plot)
Material from Matt Berger
Similarity
- Elements with the same visual properties considered to be grouped
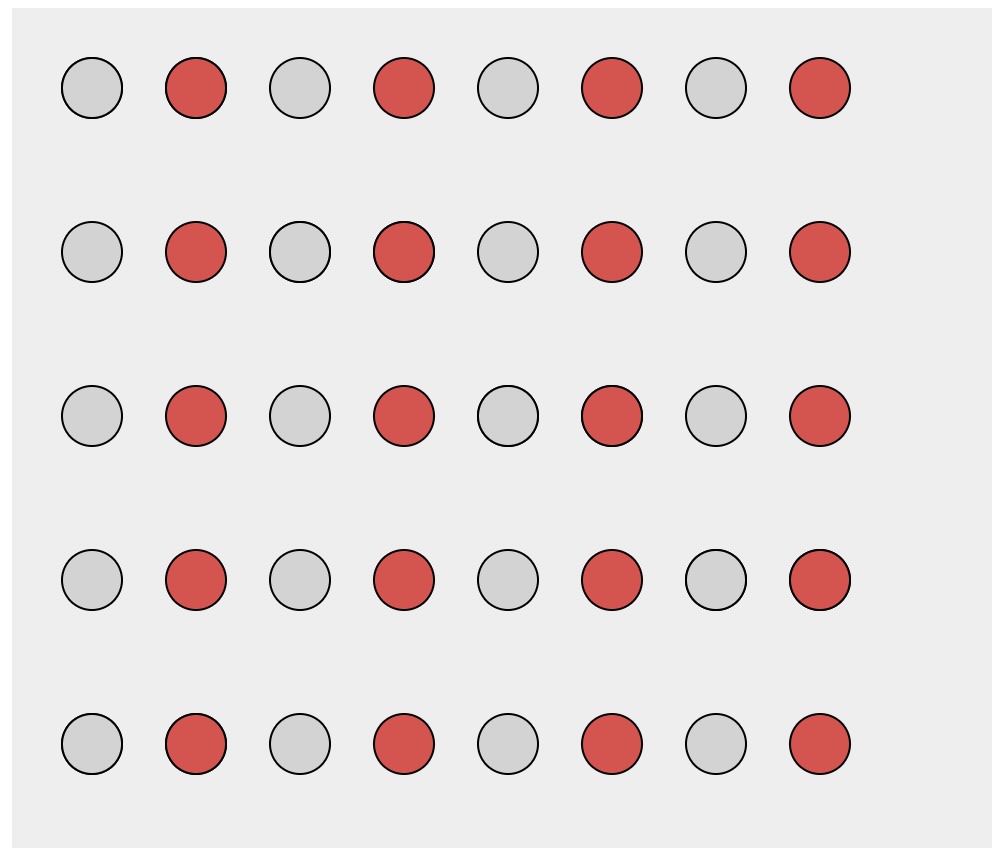
Material from Matt Berger
Similarity
- Elements with the same visual properties considered to be grouped
Material from Enrico Bertini
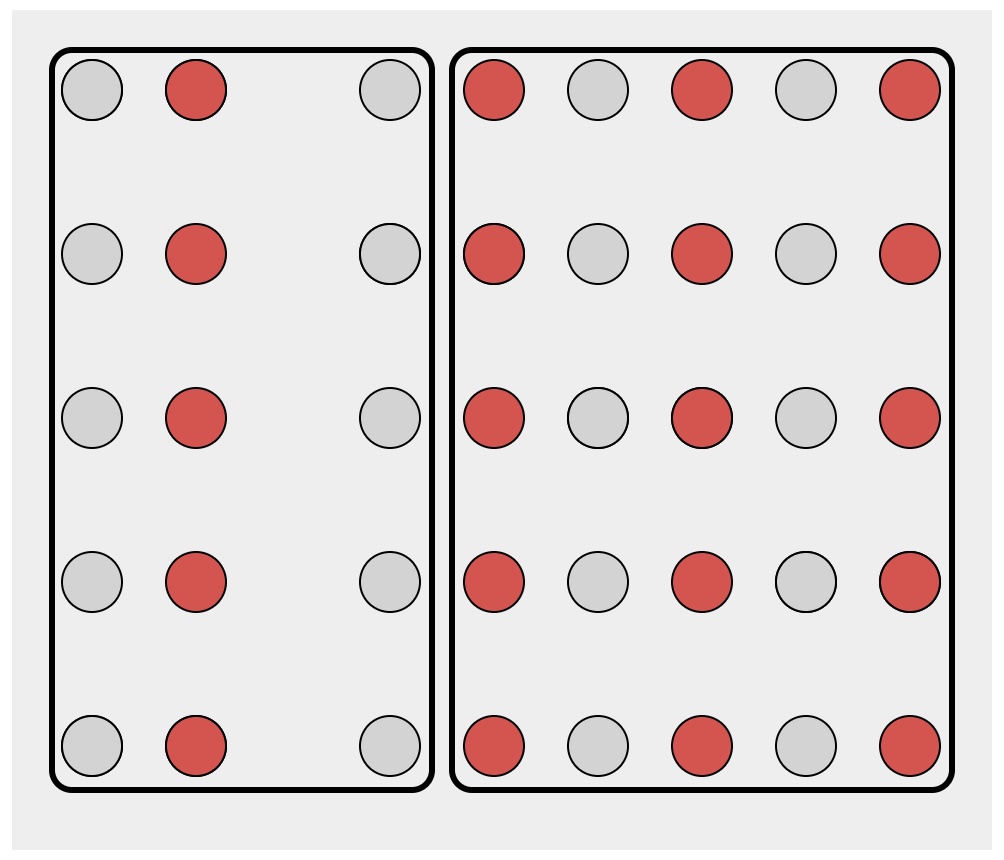
Proximity
- Elements that are of close spatial proximity are somehow grouped.

Material from Matt Berger
Proximity
- Elements that are of close spatial proximity are somehow grouped.
Material from Enrico Bertini
Enclosure
- Explicit visual encoding of enclosure also depicts grouping.
Material from Matt Berger
Enclosure
- Explicit visual encoding of enclosure also depicts grouping.
Material from Enrico Bertini
Connection
- Objects connected together are perceived as a group.
Material from Enrico Bertini
Connection
- Objects connected together are perceived as a group.
Material from Enrico Bertini
Connection
- Objects connected together are perceived as a group.
Material from Enrico Bertini
Connection
- Objects connected together are perceived as a group.
Material from Enrico Bertini
Just Noticeable Difference (JND)
In psychophysics a just-noticeable difference or JND is the amount something must be changed in order for a difference to be noticeable, detectable at least half the time.
Stevens’s power law: link
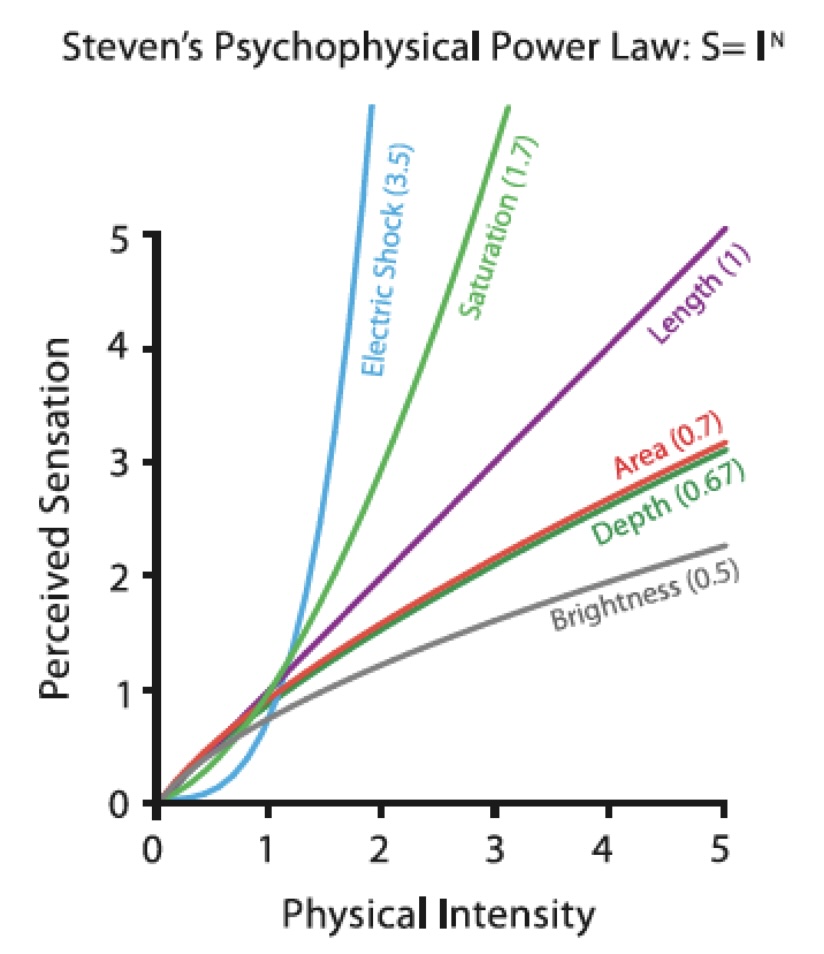
Wikipedia: link
Accuracy
- How accurately a channel can express quantitative information
Graphical Perception


Slides based on material from Prof. Enrico Bertini
Graphical Perception Experiment
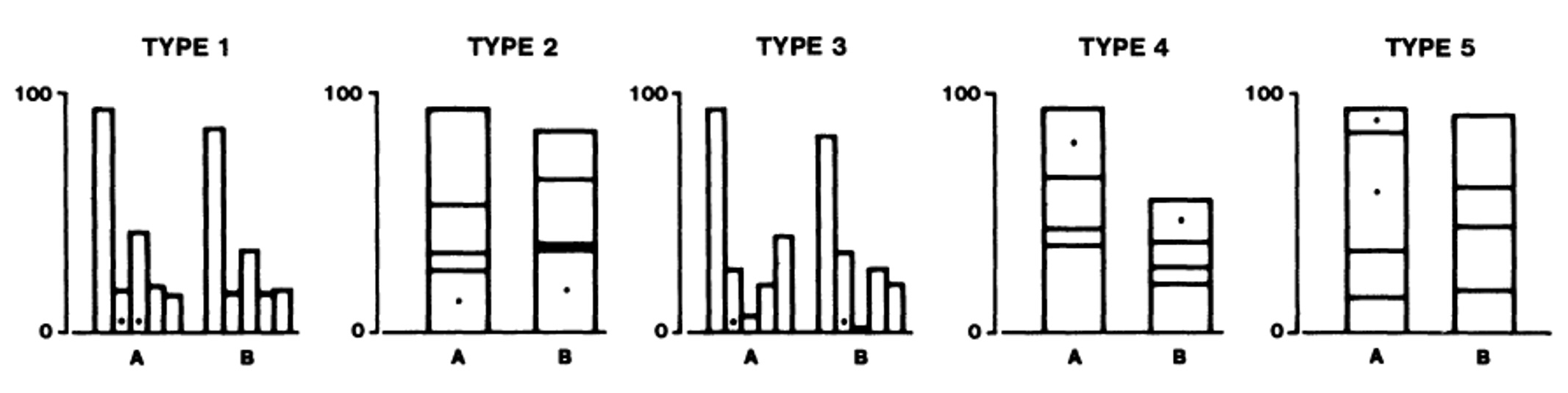
Slides based on material from Prof. Enrico Bertini
Graphical Perception Results

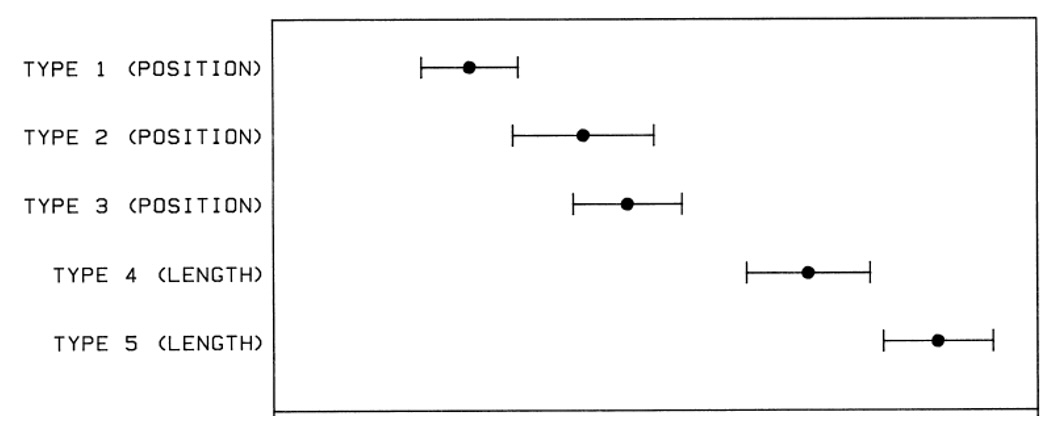
Slides based on material from Prof. Enrico Bertini
Accuracy
Position > Length and Angle > Area
Prioritize high-rank channels (with reason)
Do not expect precise judgments from low-rank channels
Slides based on material from Prof. Enrico Bertini
Effectiveness Effect
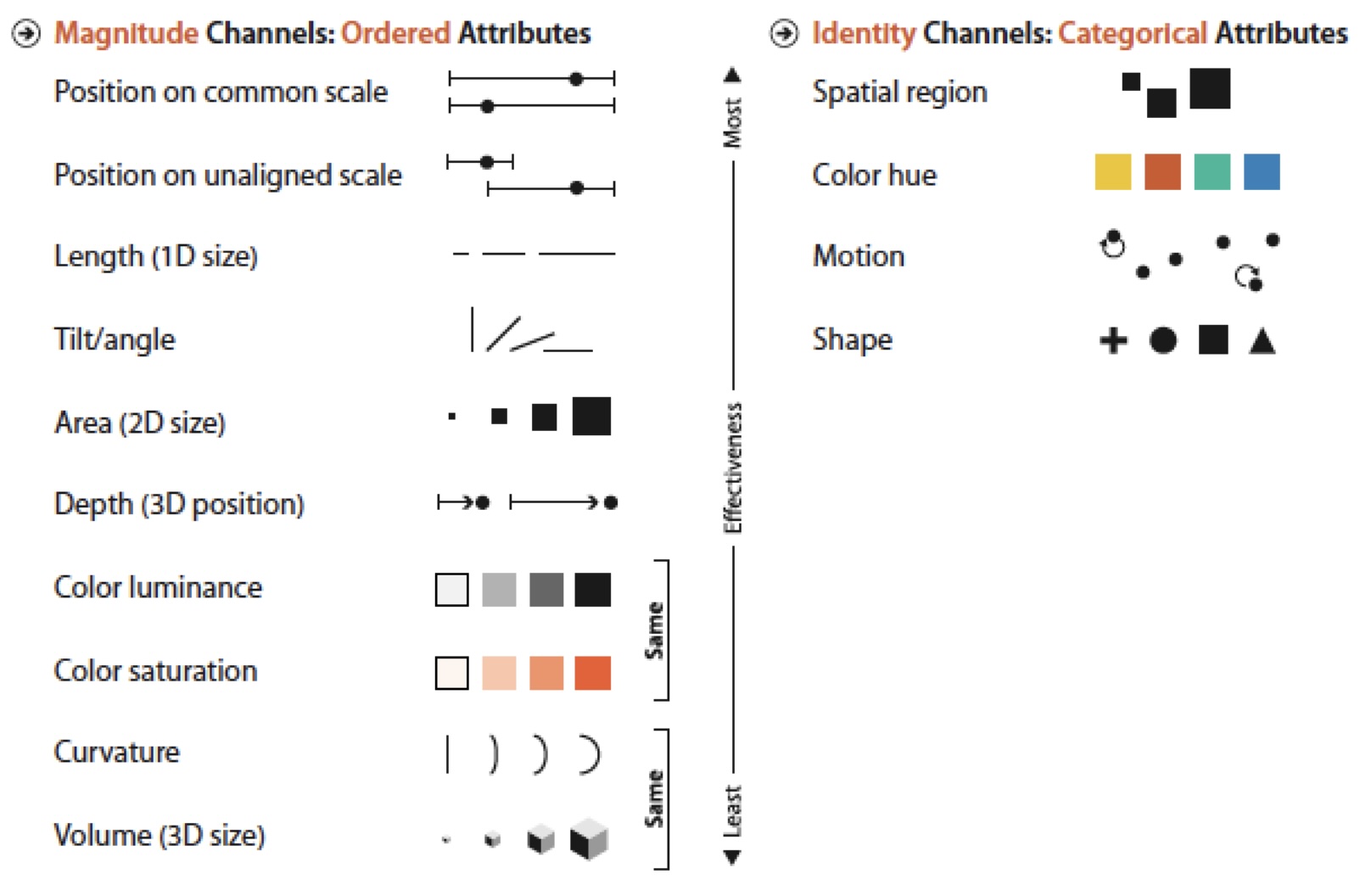
Discriminability
How many distinct values can be distinguished within a channel
It depends on:
- Channel properties
- Spatial arrangement
- Size (resolution)
- Cardinality
Warning: Do not overestimate the number of values viewers can perceive/discriminate
Slides based on material from Prof. Enrico Bertini
Discriminability
- Many channels, in particular identity channels, can only support a limited number of discriminable levels.
- Line width is one of the most limited with perhaps 3 levels.
- Using more than 5 or 6 color hues is not recommended.
- Similarly, using more than 5 or 6 symbol shapes can create difficulties.
- If the number of levels that can be represented by a channel is smaller than the number of attribute levels then some form of meaningful aggregation is needed.
Material from link
Popout
Tasks performed in less than 200 to 250 milliseconds.
Faster than eyes movement initiation.
Suggest processing by parallel low-level visual system.
Slides based on material from Prof. Enrico Bertini
Popout

Slides based on material from Prof. Enrico Bertini
Some features are not pre-attentive
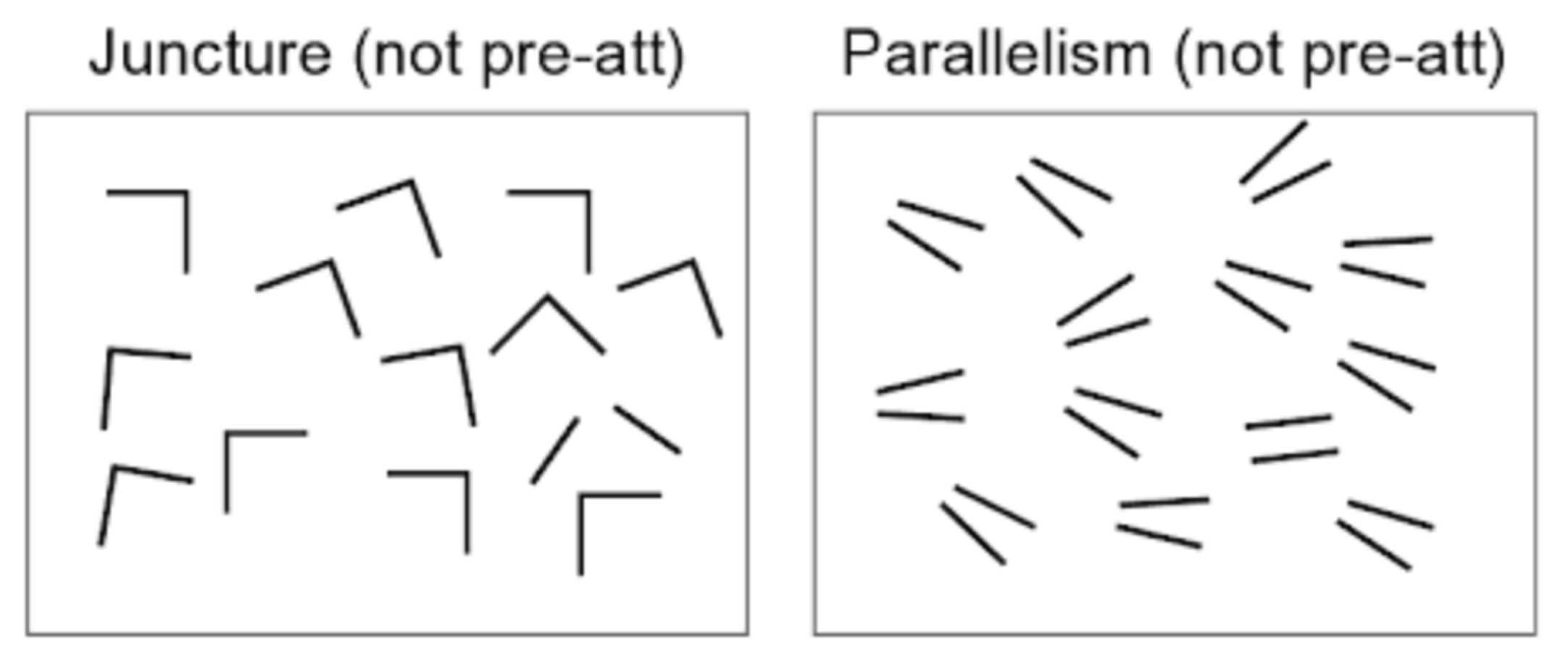
Slides based on material from Prof. Enrico Bertini
Tasks requiring the use of multiple channels are (most of the time) not preattentive
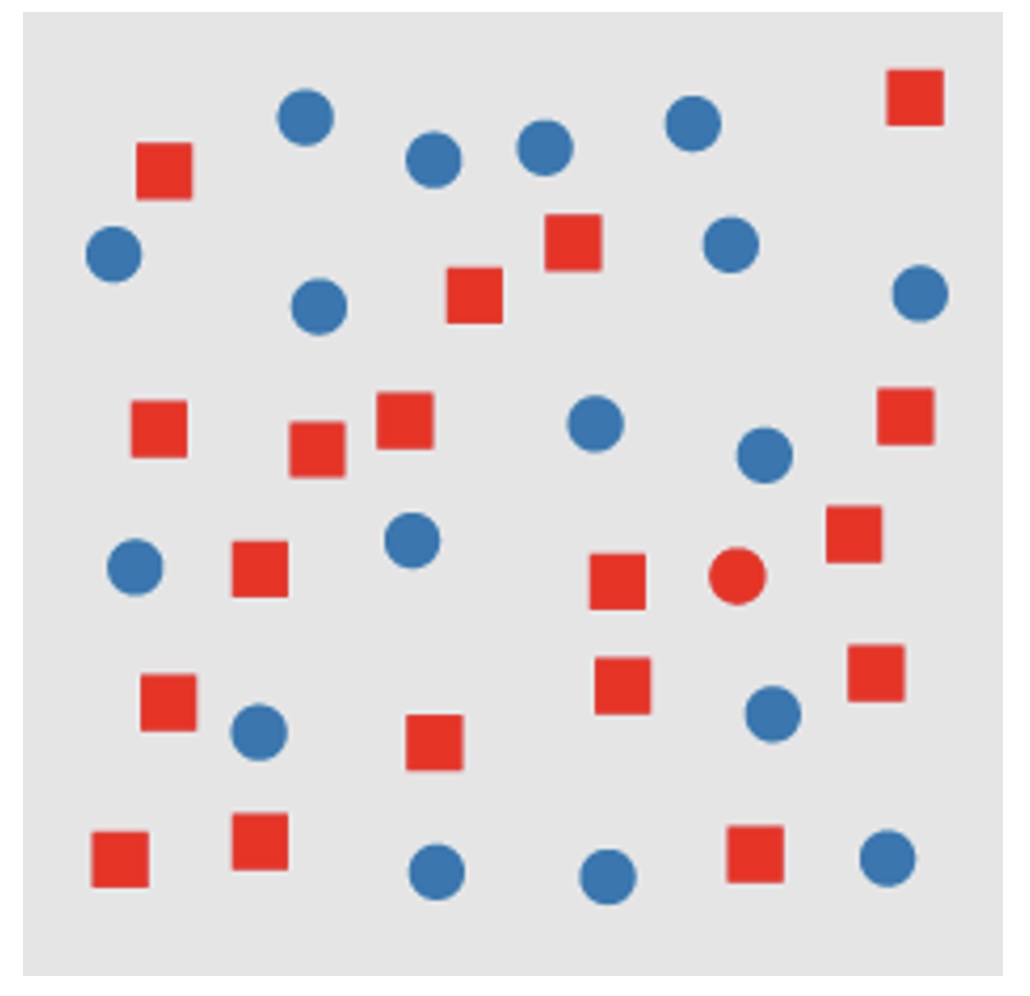
Slides based on material from Prof. Enrico Bertini
Separability
- Amount of interference between channels
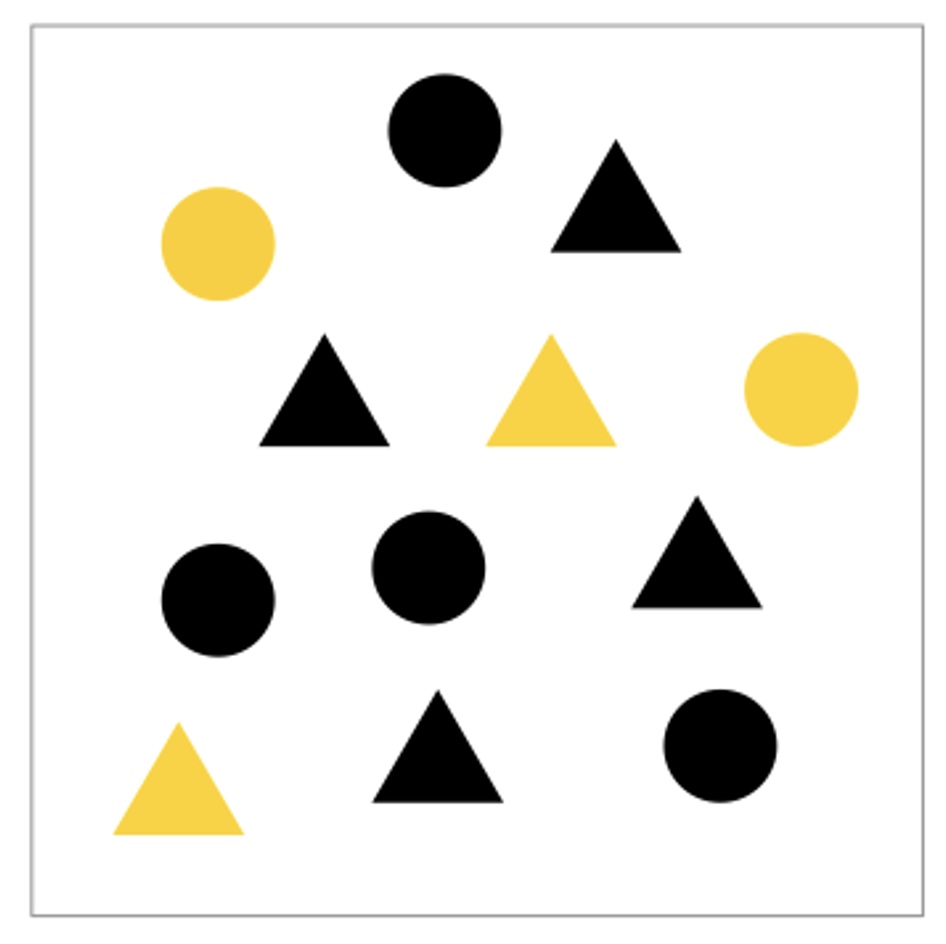

Slides based on material from Prof. Enrico Bertini
Relative vs Absolute